Alidornase alfa (PRX-110)
Alidornase alfa is a plant cell expressed recombinant human DNase I chemically modified to resist inhibition by actin, thus enhancing enzymatic activity. Recombinant human DNase I enzymatically cleaves DNA, yet its activity is inhibited by actin, which is present in the blood. In vitro studies have shown that alidornase alfa has a highly improved catalytic efficiency and affinity to DNA, compared to DNase I, even more so in the presence of actin Alidornase alfa was previously tested in Cystic Fibrosis (CF) patients in a Phase IIa trial completed in 2018. Alidornase alfa was generally well tolerated in this clinical trial with no serious adverse events reported, and all adverse events that occurred during the study were mild and transient in nature. In human sputa samples of CF patients, alidornase alfa exhibits greater activity compared to DNase I, without actin inhibition resistance, in breaking down extracellular DNA and lowering sputum viscosity Biologically active and safe in humans, alidornase alfa is being developed for other indications where it might have a potential benefit. Protalix has licensed alidornase alfa for inhaled indications to SarcoMed USA Inc , which intends to begin a clinical trial for pulmonary sarcoidosis.
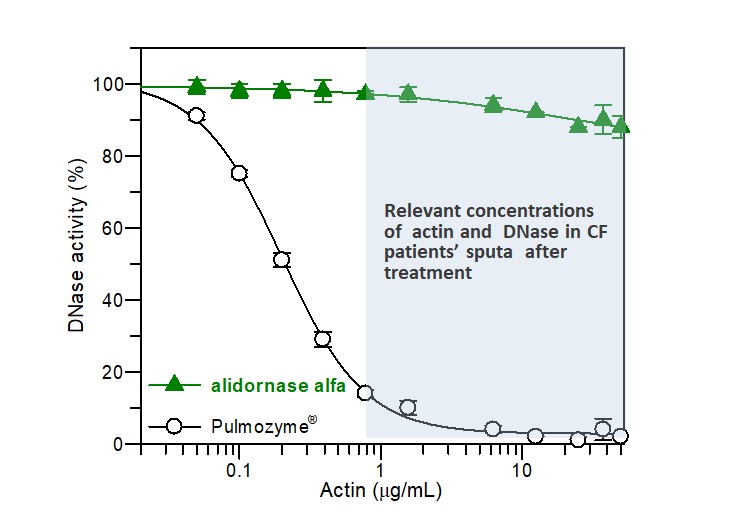

Alidornase alfa (PRX-110) remains active
Actin, a potent inhibitor of DNase I, is found in high concentration in CF patients’ sputum. As demonstrated in Figure 1, the activity of alidornase alfa, as demonstrated in in vitro studies, remains almost with no change in the relevant actin concentration found in CF patients, while Pulmozyme® is degraded significantly.
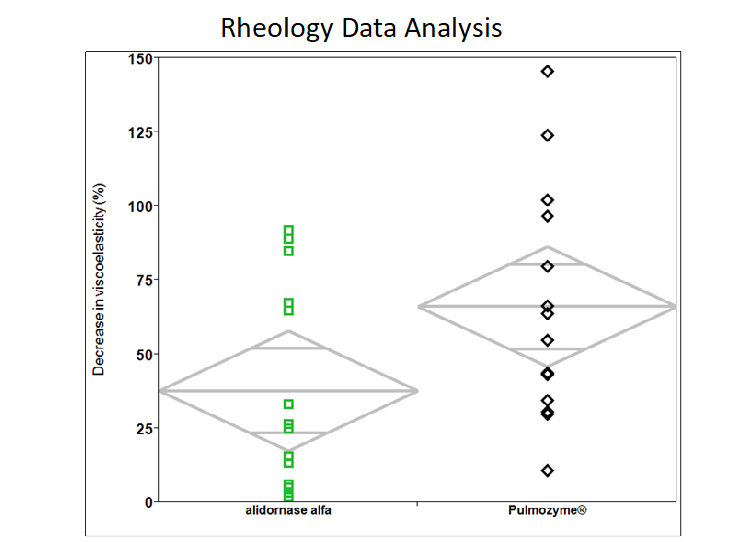

Reduction in Mucus Viscosity
Alidornase alfa has demonstrated improved disease parameters in human model sputum testing compared to Pulmozyme®. In particular, alidornase alfa has demonstrated a greater reduction in mucus viscosity in human sputum samples when compared to the currently marketed product.
